Liberia’s main trading countries
Liberia, a West African nation with a rich history, has a trading network influenced by its natural resources, economic structure, and global partnerships. Its key trading countries reflect the demand for Liberian exports like rubber, iron ore, gold, and timber, as well as its need for imported goods, such as machinery, food products, and refined petroleum.
Main Export Partners
Liberia’s exports are dominated by natural resources, with rubber and iron ore being the leading commodities. The country’s main export partners include:
1. China: A significant importer of Liberia’s iron ore, China has established itself as a key trading partner. The demand for raw materials to fuel China’s industries makes Liberia’s mineral wealth a vital component of this trade relationship.
2. India: India is a major buyer of Liberian rubber and other agricultural products. Rubber from Liberia is crucial for India’s tire and manufacturing industries, ensuring strong trade ties.
3. European Union (EU): Countries like Germany and Belgium import Liberian timber and agricultural products. These exports cater to the EU’s construction and industrial markets, making Europe an essential destination for Liberian goods.
4. United States: The U.S. has historical ties with Liberia and remains a buyer of its natural resources, especially rubber. The longstanding relationship between the two countries fosters a steady flow of trade.
5. Switzerland: Known for its role in the global gold market, Switzerland is a significant importer of Liberian gold. This relationship underscores Liberia’s position as a key supplier of precious metals.
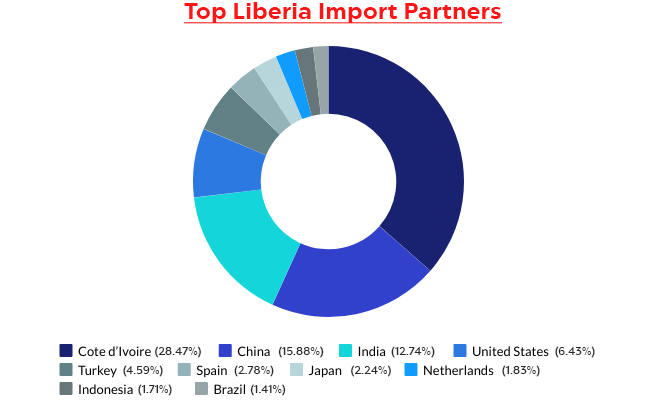
Main Import Partners
Liberia relies on imports to meet domestic needs, particularly for food, machinery, and refined petroleum. Key import partners include:
1. China: Beyond being an export destination, China also serves as a major supplier of machinery, electronics, and manufactured goods to Liberia. This dual relationship strengthens economic ties between the two nations.
2. United States: The U.S. provides Liberia with essential imports such as machinery, vehicles, and industrial equipment. This partnership supports Liberia’s infrastructure development and industrial growth.
3. European Union (EU): EU countries supply Liberia with refined petroleum, food products, and other consumer goods. The EU’s role as a supplier complements its position as a buyer of Liberian exports.
4. Ivory Coast and Ghana: These neighboring West African nations are important sources of food products and consumer goods for Liberia. Regional trade enhances economic integration within the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
5. Japan and South Korea: Both countries export vehicles and electronics to Liberia, contributing to the development of the transportation and technology sectors.
Trade Challenges and Opportunities
Liberia’s trade is shaped by its reliance on raw materials, making it vulnerable to global commodity price fluctuations. Additionally, infrastructural limitations, such as inadequate port facilities and roads, pose challenges to trade efficiency. However, Liberia’s membership in regional and international trade agreements, such as ECOWAS and the World Trade Organization (WTO), provides opportunities to diversify its trade relationships and improve market access.
Conclusion
Liberia’s main trading countries reflect its position as a resource-rich nation striving for economic growth. Countries like China, India, the U.S., and the EU play crucial roles in its trade dynamics, both as buyers of exports and suppliers of essential imports. Strengthening these relationships while diversifying its economy can help Liberia achieve greater economic stability and prosperity.